You are looking at the documentation of a prior release. To read the documentation of the latest release, please
visit here.
Monitoring KubeStash with builtin Prometheus
This tutorial will show you how to configure builtin Prometheus scraper to monitor KubeStash.
To keep Prometheus resources isolated, we are going to use a separate namespace called monitoring to deploy the Prometheus server and its respective resources. Create the namespace as below if you haven’t done already.
$ kubectl create ns monitoring
namespace/monitoring created
Enable Monitoring in KubeStash
During the installation of KubeStash, all the necessary MetricsConfigurations are created. You can find these MetricsConfigurations using the following command:
$ kubectl get metricsconfigurations
NAME APIVERSION KIND AGE
kubestash-appscode-com-backupconfiguration core.kubestash.com/v1alpha1 BackupConfiguration 113m
kubestash-appscode-com-backupsession core.kubestash.com/v1alpha1 BackupSession 113m
kubestash-appscode-com-backupstorage storage.kubestash.com/v1alpha1 BackupStorage 113m
kubestash-appscode-com-repository storage.kubestash.com/v1alpha1 Repository 113m
kubestash-appscode-com-restoresession core.kubestash.com/v1alpha1 RestoreSession 113m
kubestash-appscode-com-snapshot storage.kubestash.com/v1alpha1 Snapshot 113m
Next, you need to install Panopticon. You can install Panopticon using the following commands:
$ helm repo add appscode https://charts.appscode.com/stable/
$ helm repo update
$ helm install panopticon appscode/panopticon -n kubeops \
--create-namespace \
--set monitoring.enabled=true \
--set monitoring.agent=prometheus.io/builtin \
--set-file license=/path/to/license-file.txt
Deploy Prometheus Server
In this section, we are going to configure & deploy a Prometheus server to scrape KubeStash metrics using the Panopticon Service. We are going to deploy the Prometheus server in monitoring namespace.
Create RBAC:
Now, let’s create the necessary RBAC stuffs for the Prometheus server,
$ kubectl apply -f https://github.com/stashed/docs/raw/v2025.2.10/docs/guides/monitoring/prom-builtin/examples/prom-rbac.yaml
clusterrole.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/prometheus created
serviceaccount/prometheus created
clusterrolebinding.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/prometheus created
Create ConfigMap:
Now, create a ConfigMap with the necessary scraping configuration. Let’s create the ConfigMap,
$ kubectl apply -f https://github.com/stashed/docs/raw/v2025.2.10/docs/guides/monitoring/prom-builtin/examples/prom-configmap.yaml
configmap/prometheus-config created
Deploy Prometheus:
Now, we are ready to deploy our Prometheus server. YAML for the Deployment that we are going to create is shown below.
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: prometheus
namespace: monitoring
labels:
app: prometheus-demo
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app: prometheus
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: prometheus
spec:
serviceAccountName: prometheus
containers:
- name: prometheus
image: prom/prometheus:v2.28.1 #v2.47.2
args:
- "--config.file=/etc/prometheus/prometheus.yml"
- "--storage.tsdb.path=/prometheus/"
ports:
- containerPort: 9090
volumeMounts:
- name: prometheus-config
mountPath: /etc/prometheus/
- name: prometheus-storage
mountPath: /prometheus/
volumes:
- name: prometheus-config
configMap:
defaultMode: 420
name: prometheus-config
- name: prometheus-storage
emptyDir: {}
Let’s create the Deployment we have shown above,
$ kubectl apply -f https://github.com/stashed/docs/raw/v2025.2.10/docs/guides/monitoring/prom-builtin/examples/prom-deployment.yaml
deployment.apps/prometheus created
Now, wait for the Prometheus server to go into Running state,
$ kubectl get pods -n monitoring
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
prometheus-9b97877-4vkpz 1/1 Running 0 16m
Once the Prometheus server Pod goes into the Running state, it should automatically discover the Panopticon endpoints using the configuration we have provided in the ConfigMap.
Verify Monitoring Metrics
Now, we are going to verify whether the Prometheus server has discovered the Panopticon endpoints or not. The Prometheus server we have deployed above is running on port 9090. We are going to use port forwarding to access the Prometheus web UI.
Run following command on a separate terminal to port-forward the Prometheus server Pod,
$ kubectl port-forward -n monitoring prometheus-9b97877-4vkpz 9090
Forwarding from 127.0.0.1:9090 -> 9090
Forwarding from [::1]:9090 -> 9090
Now, we can access the web UI at localhost:9090. Open http://localhost:9090/targets in your browser. You should see Panopticon service as targets.
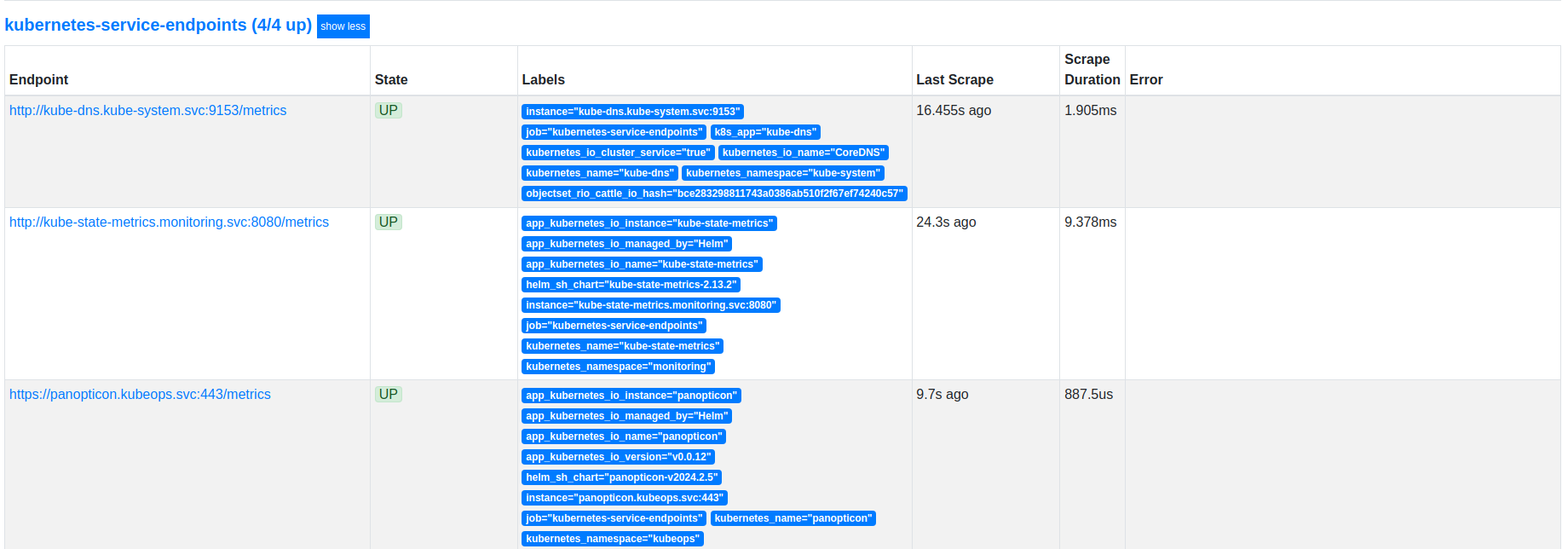
As you can see from the above image that the Prometheus server has successfully discovered the Panopticon endpoints. Now, if you perform backup and restore operations, you should see the respective metrics have been scrapped by the Prometheus server.
Cleanup
To cleanup the Kubernetes resources created by this tutorial, run:
kubectl delete clusterrole prometheus
kubectl delete clusterrolebinding prometheus
kubectl delete serviceaccount/prometheus -n monitoring
kubectl delete configmap/prometheus-config -n monitoring
kubectl delete deployment prometheus -n monitoring
kubectl delete ns monitoring
To uninstall KubeStash follow this guide.














