You are looking at the documentation of a prior release. To read the documentation of the latest release, please
visit here.
Backup YAMLs of an Application using KubeStash
This guide will show you how you can take a backup of the YAMLs of an application along with it’s dependant using KubeStash.
Before You Begin
- At first, you need to have a Kubernetes cluster, and the
kubectlcommand-line tool must be configured to communicate with your cluster. - Install KubeStash in your cluster following the steps here.
- Install KubeStash
kubectlplugin in your local machine following the steps here. - If you are not familiar with how KubeStash backup the resource YAMLs, please check the following guide here.
You have to be familiar with the following custom resources:
To keep things isolated, we are going to use a separate namespace called demo throughout this tutorial. Create the demo namespace if you haven’t created it already.
$ kubectl create ns demo
namespace/demo created
Note: YAML files used in this tutorial are stored here.
Prepare Backend
Now, we are going backup of the YAMLs of an application to a GCS bucket using KubeStash. For this, we have to create a Secret with necessary credentials and a BackupStorage object. If you want to use a different backend, please read the respective backend configuration doc from here.
For GCS backend, if the bucket does not exist, KubeStash needs
Storage Object Adminrole permissions to create the bucket. For more details, please check the following guide.
Create Secret:
Let’s create a Secret named gcs-secret with access credentials of our desired GCS backend,
$ echo -n '<your-project-id>' > GOOGLE_PROJECT_ID
$ cat /path/to/downloaded/sa_key_file.json > GOOGLE_SERVICE_ACCOUNT_JSON_KEY
$ kubectl create secret generic -n demo gcs-secret \
--from-file=./GOOGLE_PROJECT_ID \
--from-file=./GOOGLE_SERVICE_ACCOUNT_JSON_KEY
secret/gcs-secret created
Create BackupStorage:
Now, create a BackupStorage custom resource specifying the desired bucket, and directory inside the bucket where the backed up data will be stored.
Below is the YAML of BackupStorage object that we are going to create,
apiVersion: storage.kubestash.com/v1alpha1
kind: BackupStorage
metadata:
name: gcs-storage
namespace: demo
spec:
storage:
provider: gcs
gcs:
bucket: kubestash-qa
prefix: demo
secretName: gcs-secret
usagePolicy:
allowedNamespaces:
from: All
default: true
deletionPolicy: WipeOut
Let’s create the BackupStorage object that we have shown above,
$ kubectl apply -f https://github.com/kubestash/docs/raw/v2024.9.30/docs/guides/kubedump/application/examples/backupstorage.yaml
backupstorage.storage.kubestash.com/gcs-repo created
Now, we are ready to backup our application yaml resources.
Create RetentionPolicy:
Now, we have to create a RetentionPolicy object to specify how the old Snapshots should be cleaned up.
Below is the YAML of the RetentionPolicy object that we are going to create,
apiVersion: storage.kubestash.com/v1alpha1
kind: RetentionPolicy
metadata:
name: demo-retention
namespace: demo
spec:
default: true
failedSnapshots:
last: 2
maxRetentionPeriod: 2mo
successfulSnapshots:
last: 5
usagePolicy:
allowedNamespaces:
from: Same
Notice the spec.usagePolicy that allows referencing the RetentionPolicy from all namespaces.For more details on configuring it for specific namespaces, please refer to the following link.
Let’s create the RetentionPolicy object that we have shown above,
$ kubectl apply -f https://github.com/kubestash/docs/raw/v2024.9.30/docs/guides/kubedump/application/examples/retentionpolicy.yaml
retentionpolicy.storage.kubestash.com/demo-retention created
Create RBAC
To take backup of the resource YAMLs of an application KubeStash creates a backup Job. This Job requires read permission for the application resources. By default, KubeStash does not grant such permissions. We have to provide the necessary permissions manually.
Here, is the YAML of the ServiceAccount, ClusterRole, and ClusterRoleBinding that we are going to use for granting the necessary permissions.
apiVersion: v1
kind: ServiceAccount
metadata:
name: cluster-resource-reader
namespace: kubestash
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRole
metadata:
name: cluster-resource-reader
rules:
- apiGroups: ["*"]
resources: ["*"]
verbs: ["get","list"]
---
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRoleBinding
metadata:
name: cluster-resource-reader
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: cluster-resource-reader
namespace: kubestash
roleRef:
kind: ClusterRole
name: cluster-resource-reader
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
Here, we have give permission to read all the cluster resources. You can restrict this permission to a particular application resources only.
Let’s create the RBAC resources we have shown above,
$ kubectl apply -f https://github.com/kubestash/docs/raw/v2024.9.30/docs/guides/kubedump/application/examples/rbac.yaml
serviceaccount/cluster-resource-reader created
clusterrole.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/cluster-resource-reader created
clusterrolebinding.rbac.authorization.k8s.io/cluster-resource-reader created
Now, we are ready for backup. In the next section, we are going to schedule a backup for our cluster resources.
Backup
Now, we have to create a BackupConfiguration custom resource targeting an application.
Lets list available Deployment in kubestash namespace.
$ kubectl get deployments -n kubestash
NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE
kubestash-kubestash-operator 1/1 1 1 19h
Here, we are going to take backup YAMLs for kubestash-kubestash-operator Deployment.
Create Secret:
We also have to create another Secret with an encryption key RESTIC_PASSWORD for Restic. This secret will be used by Restic for encrypting the backup data.
Let’s create a secret named encrypt-secret with the Restic password.
$ echo -n 'changeit' > RESTIC_PASSWORD
$ kubectl create secret generic -n demo encrypt-secret \
--from-file=./RESTIC_PASSWORD
secret/encrypt-secret created
Create BackupConfiguration
Below is the YAML of the BackupConfiguration object we are going to create to backup the YAMLs of the cluster resources,
apiVersion: core.kubestash.com/v1alpha1
kind: BackupConfiguration
metadata:
name: application-manifest-backup
namespace: demo
spec:
target:
apiGroup: apps
kind: Deployment
name: kubestash-kubestash-operator
namespace: kubestash
backends:
- name: gcs-backend
storageRef:
namespace: demo
name: gcs-storage
retentionPolicy:
name: demo-retention
namespace: demo
sessions:
- name: frequent-backup
sessionHistoryLimit: 3
scheduler:
schedule: "*/5 * * * *"
jobTemplate:
backoffLimit: 1
repositories:
- name: gcs-repository
backend: gcs-backend
directory: /deployment-manifests
encryptionSecret:
name: encrypt-secret
namespace: demo
deletionPolicy: WipeOut
addon:
name: kubedump-addon
tasks:
- name: manifest-backup
params:
includeDependants: "true"
jobTemplate:
spec:
serviceAccountName: cluster-resource-reader
Here,
spec.sessions[*].addon.namespecifies the name of theAddon.spec.sessions[*].addon.tasks[*].namespecifies the name of the backup task.spec.sessions[*].addon.jobTemplate.spec.serviceAccountNamespecifies the ServiceAccount name that we have created earlier with cluster-wide resource reading permission.
Let’s create the BackupConfiguration object we have shown above,
$ kubectl apply -f https://github.com/kubestash/docs/raw/v2024.9.30/docs/guides/kubedump/application/examples/backupconfiguration.yaml
backupconfiguration.core.kubestash.com/application-manifest-backup created
Verify Backup Setup Successful
If everything goes well, the phase of the BackupConfiguration should be in Ready state. The Ready phase indicates that the backup setup is successful.
Let’s check the Phase of the BackupConfiguration
$ kubectl get backupconfiguration -n demo
NAME PHASE PAUSED AGE
application-manifest-backup Ready 19s
Verify Repository:
Verify that the Repository specified in the BackupConfiguration has been created using the following command,
$ kubectl get repositories -n demo
NAME INTEGRITY SNAPSHOT-COUNT SIZE PHASE LAST-SUCCESSFUL-BACKUP AGE
gcs-repository Ready 28s
KubeStash keeps the backup for Repository YAMLs. If we navigate to the GCS bucket, we will see the Repository YAML stored in the demo/deployment-manifests directory.
Verify CronJob:
Verify that KubeStash has created a CronJob with the schedule specified in spec.sessions[*].scheduler.schedule field of BackupConfiguration object.
Check that the CronJob has been created using the following command,
$ kubectl get cronjob -n demo
NAME SCHEDULE SUSPEND ACTIVE LAST SCHEDULE AGE
trigger-application-manifest-backup-frequent-backup */5 * * * * False 0 <none> 45s
Wait for BackupSession:
Now, wait for the next backup schedule. You can watch for BackupSession CR using the following command,
$ watch -n 1 kubectl get backupsession -n demo -l=kubestash.com/invoker-name=application-manifest-backup
Every 1.0s: kubectl get backupsession -n demo -l=kubestash.com/invoker-name=application-manifest-backup anisur: Fri Feb 23 14:35:27 2024
NAME INVOKER-TYPE INVOKER-NAME PHASE DURATION AGE
application-manifest-backup-frequent-backup-1708677300 BackupConfiguration application-manifest-backup Succeeded 27s
Verify Backup:
When BackupSession is created, KubeStash operator creates Snapshot for each Repository listed in the respective session of the BackupConfiguration. Since we have only specified one repository in the session, at this moment we should have one Snapshot.
Run the following command to check the respective Snapshot,
$ kubectl get snapshots -n demo
NAME REPOSITORY SESSION SNAPSHOT-TIME DELETION-POLICY PHASE AGE
gcs-repository-application-manifckup-frequent-backup-1708677300 gcs-repository frequent-backup 2024-02-23T08:35:00Z Delete Succeeded 43s
Now, if we navigate to the GCS bucket, we will see the backed up data stored in the demo/deployment-manifests/repository/v1/frequent-backup/manifest directory. KubeStash also keeps the backup for Snapshot YAMLs, which can be found in the kubestash-qa/demo/deployment-manifests/repository/snapshots directory.
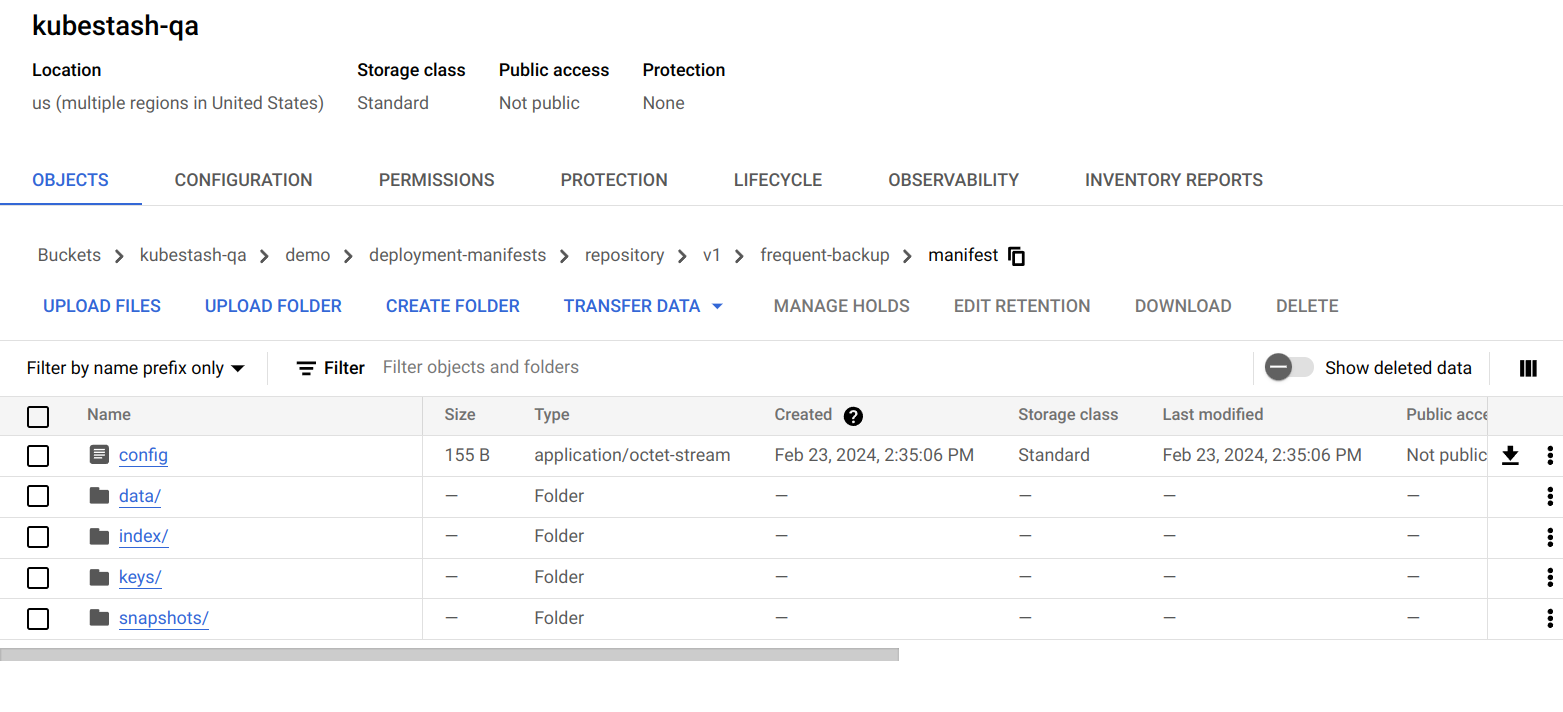
Note: KubeStash stores all dumped data encrypted in backup directory, meaning it remains unreadable until decrypted.
Restore
KubeStash does not provide any automatic mechanism to restore the cluster resources from the backed-up YAMLs. Your application might be managed by Helm or by an operator. In such cases, just applying the YAMLs is not enough to restore the application. Furthermore, there might be an order issue. Some resources must be applied before others. It is difficult to generalize and codify various application-specific logic.
Therefore, it is the user’s responsibility to download the backed-up YAMLs and take the necessary steps based on his application to restore it properly.
Download the YAMLs
KubeStash provides a kubectl plugin for making it easy to download a snapshot locally.
Now, let’s download the latest Snapshot from our backed-up data into the $HOME/Downloads/kubestash/applications/kubestash/kubestash-kubestash-operator folder of our local machine.
$ kubectl kubestash download gcs-repository-application-manifckup-frequent-backup-1708677300 --namespace=demo --destination=$HOME/Downloads/kubestash/applications/kubestash/kubestash-kubestash-operator
Now, lets use tree command to inspect downloaded YAMLs files.
$ tree $HOME/Downloads/kubestash/applications/kubestash/kubestash-kubestash-operator
/home/anisur/Downloads/kubestash/applications/kubestash/kubestash-kubestash-operator
└── gcs-repository-application-manifckup-frequent-backup-1708677300
└── manifest
└── tmp
└── manifest
├── kubestash-kubestash-operator.yaml
└── ReplicaSet
└── kubestash-kubestash-operator-7bc7564b69
├── kubestash-kubestash-operator-7bc7564b69.yaml
└── Pod
└── kubestash-kubestash-operator-7bc7564b69-2frcq
└── kubestash-kubestash-operator-7bc7564b69-2frcq.yaml
8 directories, 3 files
As you can see that the Deployment has been backed up along with it’s ReplicaSet and Pods.
Let’s inspect the YAML of kubestash-kubestash-operator.yaml file,
$ cat /home/anisur/Downloads/kubestash/applications/kubestash/kubestash-kubestash-operator/gcs-repository-application-manifckup-frequent-backup-1708677300/manifest/tmp/manifest/kubestash-kubestash-operator.yaml
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
annotations:
deployment.kubernetes.io/revision: "1"
meta.helm.sh/release-name: kubestash
meta.helm.sh/release-namespace: kubestash
labels:
app.kubernetes.io/instance: kubestash
app.kubernetes.io/managed-by: Helm
app.kubernetes.io/name: kubestash-operator
app.kubernetes.io/version: v0.5.0
helm.sh/chart: kubestash-operator-v0.5.0
name: kubestash-kubestash-operator
namespace: kubestash
spec:
progressDeadlineSeconds: 600
replicas: 1
revisionHistoryLimit: 10
selector:
matchLabels:
app.kubernetes.io/instance: kubestash
app.kubernetes.io/name: kubestash-operator
strategy:
rollingUpdate:
maxSurge: 25%
maxUnavailable: 25%
type: RollingUpdate
template:
metadata:
annotations:
checksum/apiregistration.yaml: 62af9aba894e98a7dc849e63a31ef52d6c3b459df8d2242e71cc72e458553d11
labels:
app.kubernetes.io/instance: kubestash
app.kubernetes.io/name: kubestash-operator
spec:
containers:
- args:
- run
- --config=/var/config/config.yaml
- --license-file=/var/run/secrets/appscode/license/key.txt
env:
- name: POD_NAME
valueFrom:
fieldRef:
apiVersion: v1
fieldPath: metadata.name
- name: POD_NAMESPACE
valueFrom:
fieldRef:
apiVersion: v1
fieldPath: metadata.namespace
image: ghcr.io/kubestash/kubestash:v0.5.0
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
name: operator
ports:
- containerPort: 9443
name: webhook-server
protocol: TCP
resources:
requests:
cpu: 100m
securityContext:
allowPrivilegeEscalation: false
capabilities:
drop:
- ALL
readOnlyRootFilesystem: true
runAsNonRoot: true
runAsUser: 65534
terminationMessagePolicy: File
volumeMounts:
- mountPath: /kubestash-tmp
name: kubestash-tmp-volume
- mountPath: /var/serving-cert
name: serving-cert
readOnly: true
- mountPath: /var/config
name: config
- mountPath: /var/run/secrets/appscode/license
name: license
- args:
- --secure-listen-address=0.0.0.0:8443
- --upstream=http://127.0.0.1:8080/
- --logtostderr=true
- --v=10
image: ghcr.io/appscode/kube-rbac-proxy:v0.11.0
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
name: kube-rbac-proxy
ports:
- containerPort: 8443
name: https
protocol: TCP
resources: {}
securityContext:
allowPrivilegeEscalation: false
capabilities:
drop:
- ALL
readOnlyRootFilesystem: true
runAsNonRoot: true
runAsUser: 65534
terminationMessagePolicy: File
nodeSelector:
kubernetes.io/os: linux
restartPolicy: Always
schedulerName: default-scheduler
securityContext:
fsGroup: 65535
serviceAccount: kubestash-kubestash-operator
serviceAccountName: kubestash-kubestash-operator
volumes:
- emptyDir: {}
name: kubestash-tmp-volume
- name: serving-cert
secret:
defaultMode: 420
secretName: kubestash-kubestash-operator-webhook-cert
- configMap:
defaultMode: 420
name: kubestash-kubestash-operator-config
name: config
- name: license
secret:
defaultMode: 420
secretName: kubestash-kubestash-operator-license
Now, you can use these YAML files to re-create your desired application.
Cleanup
To clean up the Kubernetes resources created by this tutorial, run:
kubectl delete -n demo backupconfiguration application-manifest-backup
kubectl delete -n kubestash serviceaccount cluster-resource-reader
kubectl delete clusterrole cluster-resource-reader
kubectl delete clusterrolebinding cluster-resource-reader
kubectl delete retentionPolicy -n demo demo-retention
kubectl delete -n demo backupstorage gcs-storage
kubectl delete secret -n demo encrypt-secret
kubectl delete secret -n demo gcs-secret














